Optimization of In-vivo Monitoring Program for Radiation Emergency Response
Article information
Abstract
Background
In case of radiation emergencies, internal exposure monitoring for the members of public will be required to confirm internal contamination of each individual. In-vivo monitoring technique using portable gamma spectrometer can be easily applied for internal exposure monitoring in the vicinity of the on-site area.
Materials and Methods
In this study, minimum detectable doses (MDDs) for 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I were calculated adjusting minimum detectable activities (MDAs) from 50 to 1,000 Bq to find out the optimal in-vivo counting condition. DCAL software was used to derive retention fraction of Cs and I isotopes in the whole body and thyroid, respectively. A minimum detectable level was determined to set committed effective dose of 0.1 mSv for emergency response.
Results and Discussion
We found that MDDs at each MDA increased along with the elapsed time. 1,000 Bq for 134Cs and 137Cs, and 100 Bq for 131I were suggested as optimal MDAs to provide in-vivo monitoring service in case of radiation emergencies.
Conclusion
In-vivo monitoring program for emergency response should be designed to achieve the optimal MDA suggested from the present work. We expect that a reduction of counting time compared with routine monitoring program can achieve the high throughput system in case of radiation emergencies.
Introduction
Internal exposure for the members of public as well as radiation workers can be caused by accidental releasing of radioactive materials in nuclear and radiation accidents. These individuals will need to be quickly evaluated for radioactive contamination. Individual monitoring for the members of public is essential to confirm health effects of them in case of radiation emergencies. In general, whole body counting or urine bioassays are used for routine monitoring program of internal exposure of radiation workers. However, another less-sensitive method to assess internal contamination levels for a large number of people in a short period of time has to be taken into account in case of radiation emergencies such as nuclear accidents or Radiological Dispersal Device (RDD) event [1]. It would be desirable to use a simple method to rapidly screen individuals in the field. The initial field screening can help identify individuals who are highly contaminated and prioritize ones for further evaluation and more definitive treatment [1].
In-vivo monitoring technique using portable gamma spectrometer can be applied for internal exposure monitoring in the field because portable detectors can be easily transported to the on-site area and do not require assembly. Therefore, in-vivo monitoring program has to be optimized to be properly used at the on-site area for the purpose of radiation emergency response.
The objective of this study is to derive minimum detectable doses (MDDs) along with minimum detectable activity (MDA) using the dosimetric information of 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I which are representative gamma-emitting radionuclides causing internal exposure of the members of public following nuclear and radiation accidents. And we suggested the optimal MDA and monitoring period for in-vivo monitoring of 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I following such accidents and optimized in-vivo monitoring program using portable NaI gamma spectrometer to be applied for radiation emergency response.
Materials and Methods
1. General MDAs of the concerned radionuclides
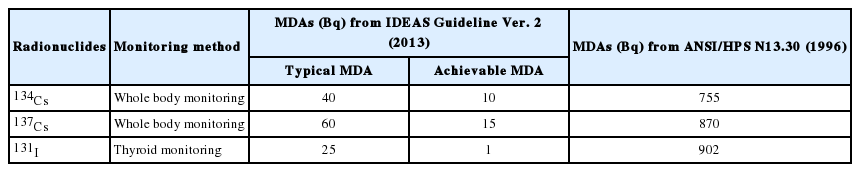
MDA is one of the important parameters to represent the performance of the radiation measurement system. The MDA is determined by the counting efficiency, counting time, emission yield, and net count level of blank sample in the region of interest (ROI). In routine radiobioassay program, typical and achievable MDAs were provided from IDEAS guideline (General guidelines for the estimation of committed effective dose from incorporation monitoring data) reported by the EURADOS [2]. In this study, we selected the concerned radionucldies which can be released to the environments and cause internal exposure of general public as well as radiation workers in case of radiation accidents. 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I were determined as the concerned radionuclides in the present work. American National Standard Institute (ANSI) also suggested the MDAs for direct radiobioassay, also known as in-vivo measurement, to be applied for routine monitoring program of internal exposure [3]. The MDAs selected from ANSI are relatively higher than those provided by EURADOS. The MDAs of these radionuclides for the in-vivo measurement are summarized in Table 1.
2. Calculation of MDDs along with the MDAs
MDDs for 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I were calculated adjusting MDAs from 50 to 1,000 Bq to find out the optimal in-vivo monitoring condition. In general, committed effective dose (CED) can be calculated as following simple equation:
where, DCC is dose conversion coefficient [Sv·Bq−1], M is measurement quantities of in-vivo monitoring [Bq], and m(t) is bioassay function representing retention fraction as a function of time t after intake [Bq·Bq-intake−1]. Then MDD can be derived as below:
In this study, we used DCAL software [4], which was developed at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory, to obtain the bioassay function of 134Cs and 137Cs in the whole body and 131I in the thyroid. Elapsed time after initial intake was considered for 365 d when we calculated the retention fraction of each radionuclide. DCCs of the members of public were used from ICRP 72 [5] in which age-dependent dose coefficients were provided from intake of radionuclides. Only inhalation was employed as a pathway of intake of the concerned radionuclides. And 10-yr old child and adult were used as age group of the public in this calculation. Table 2 shows the biokinetic parameters and DCCs used in this study. In order to find out the optimal MDA level for emergency response, MDDs were calculated adjusting MDAs from 50 to 1,000 Bq.
3. Evaluation of MDA using portable in-vivo counter
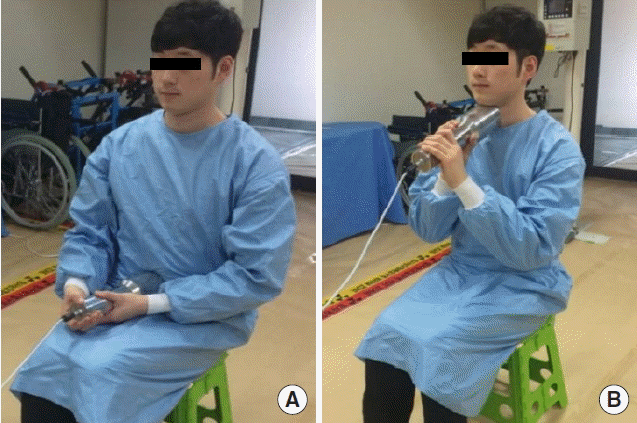
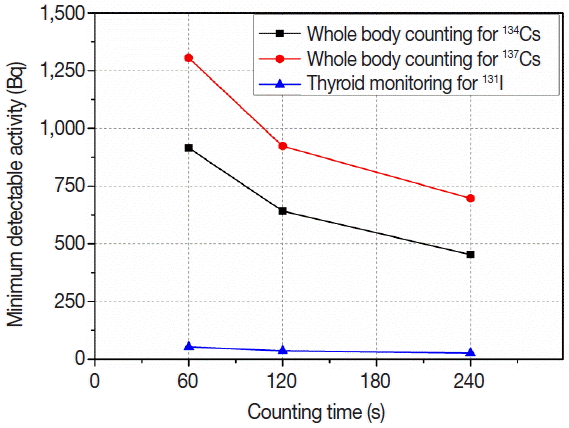
We used portable 3×3 inch NaI gamma spectrometer (RIIDEYE-M-G3, Thermo, Waltham, MA) to quantify the MDA of 134Cs, 137Cs and 131I. Counting geometries shown in Figure 1 were applied to measure radioactivity retained in whole body and thyroid, respectively. And we used BOMAB (Bottle Manikin Absorption) phantom [6] and IAEA/ANSI neck phantom [7] including mixed gamma-emitting radionuclides as a certified reference material (CRM) for the calibration of two counting geometries, whole body counting and thyroid monitoring, respectively. Counting time was employed to be 60, 120, 240 s for each counting geometry. We repeatedly measured the activity of the blank sample 5 times for each counting time and evaluated the averaged MDA of 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I depending on the counting time. After that, we compared the evaluated MDA with the suggested optimal MDAs to test the acceptance of the optimal MDA.
Results and Discussion
1. Derived bioassay functions and MDDs
Bioassay functions, m(t), as the retention fraction for 365 day after initial intake were calculated using the DCAL software. Figure 2 shows bioassay functions of 10-yr old child and adult for 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I. Bioassay functions during the elapsed period showed the similar pattern between 134Cs and 137Cs since the biokinetic model and chemical properties are almost same for Cs isotopes. From the calculation results of Cs isotopes, we verified that retention fraction of 10-yr old child decreased more rapidly than adult. On the other hand, bioassay function in the thyroid for 131I showed the different pattern with Cs isotopes. Retention fraction in the thyroid did not have a significant difference between 10-yr old child and adult. The faction in the thyroid showed the high peak around 1.2 d after intake and very sharply decreased to 10−5 within 100 d.
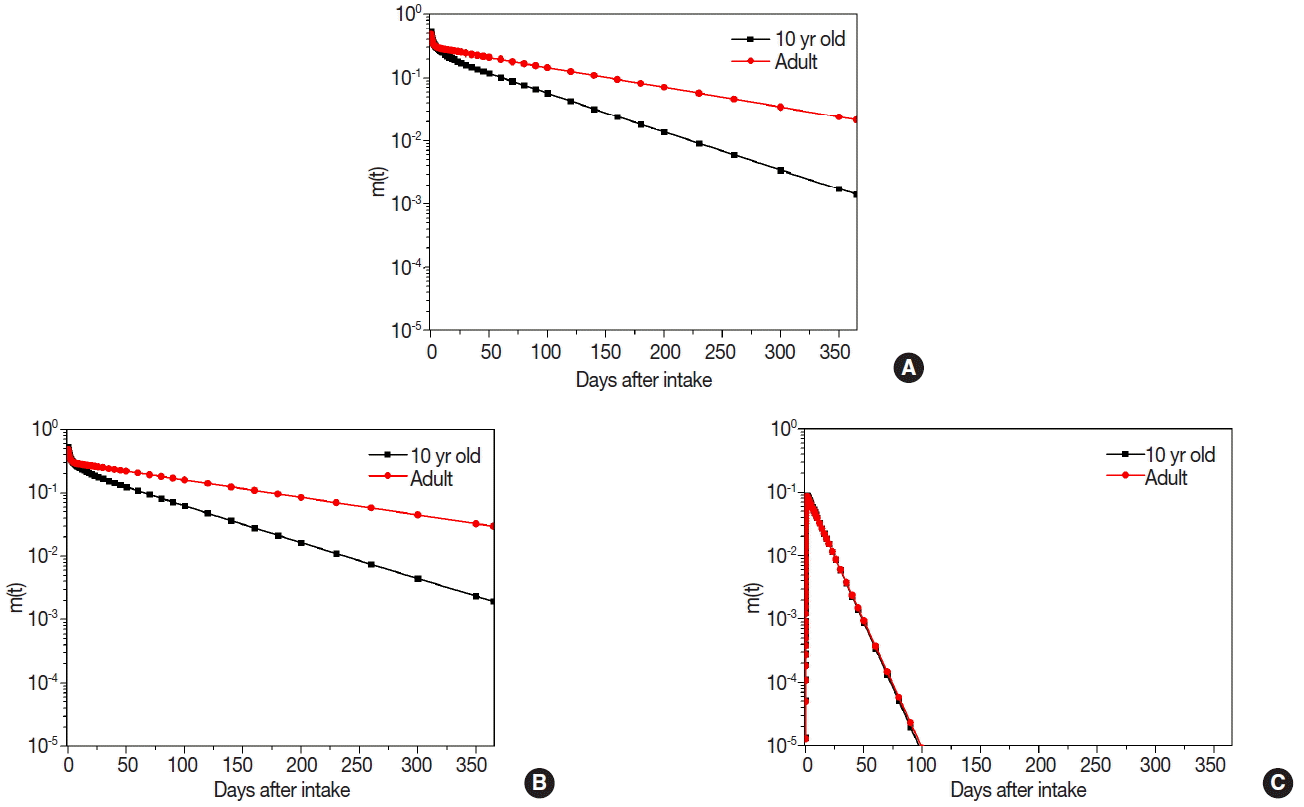
Bioassay functions of concerned radionuclides: (A) Total body retention fraction of 134Cs, (B) Total body retention fraction of 137Cs, and (C) Thyroid retention fraction of 131I.
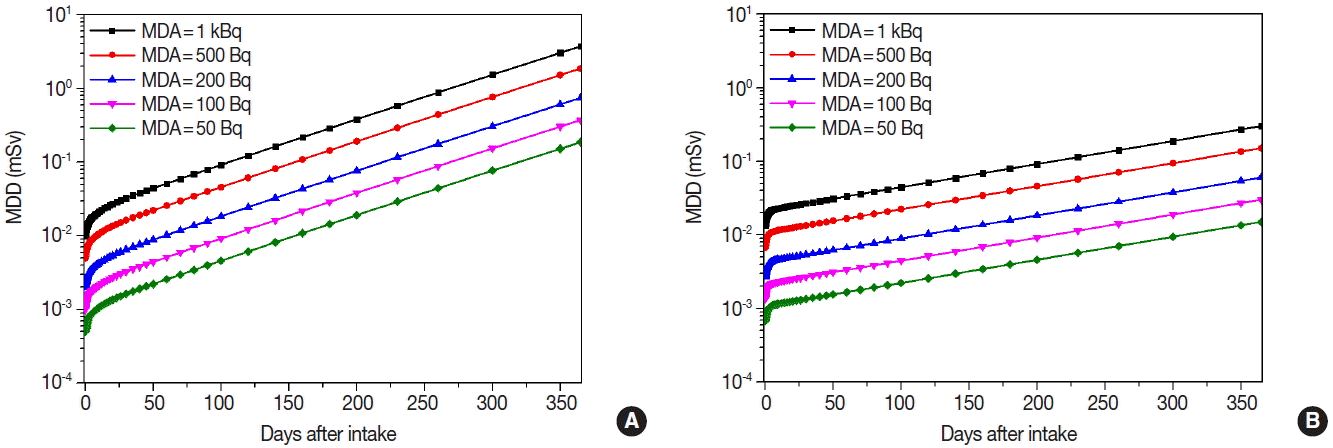
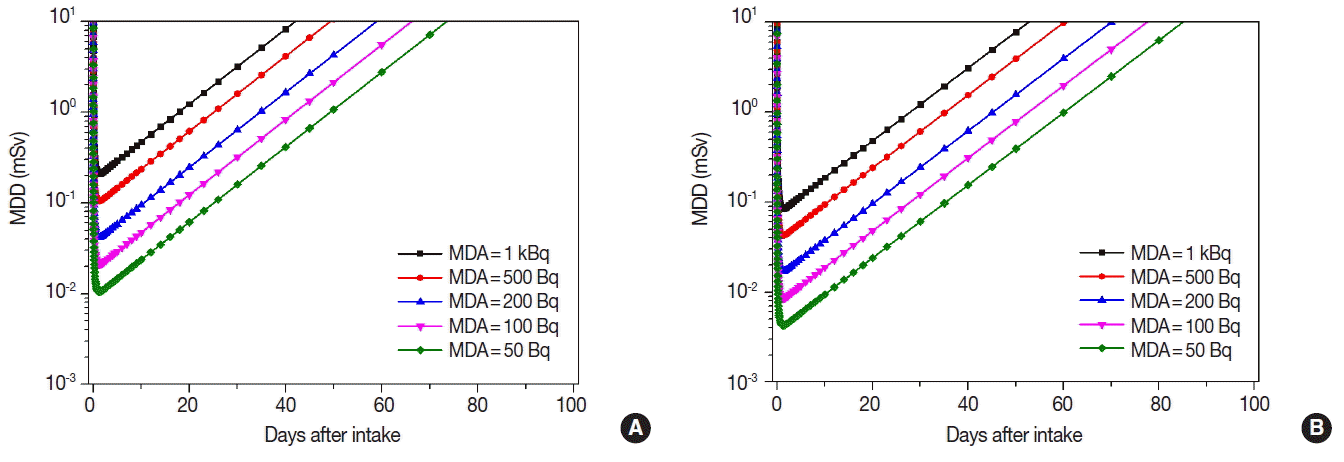
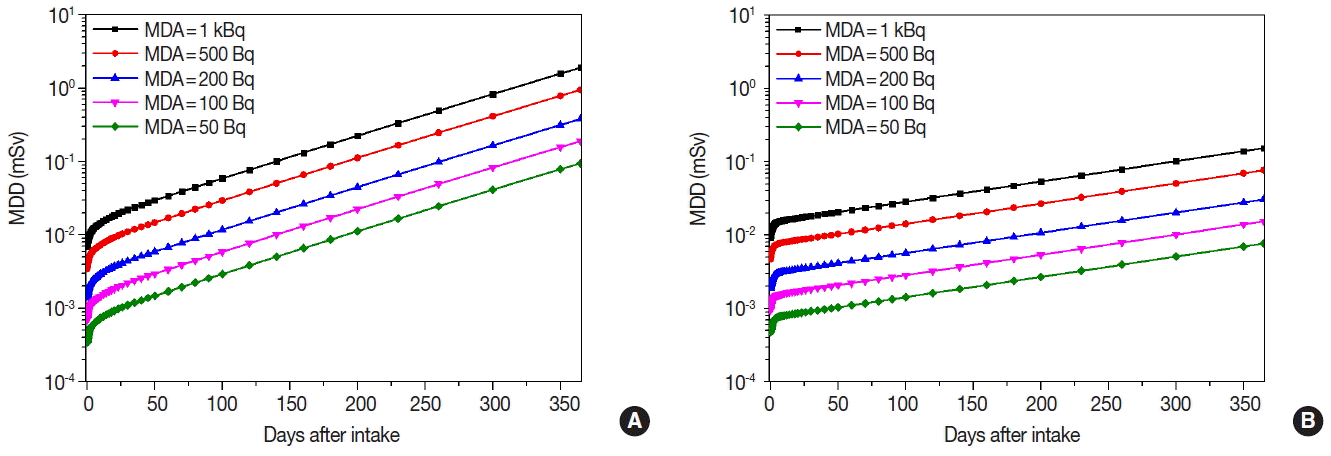
Figures 3 to 5 show the MDDs depending on the age and the MDAs for 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I. MDDs of 134Cs were slightly higher than those of 137Cs for each age group. Even though their bioassay functions showed the similar pattern, MDDs of 134Cs were 1.48 times higher than those of 137Cs since the DCCs of 134Cs are higher than those of 137Cs.
We found that MDDs increased not only when the elapsed time passed after the initial intake of the concerned radionuclides but also while the MDAs increased from 50 to 1,000 Bq. In case of 137Cs, MDDs for 10-yr old child increased more rapidly than adult because the retention fraction for 10-yr old child showed to be decreased more rapidly after the intake. In case of 131I, MDDs for 10-yr old child were 2.73 times higher than adult since the DCCs of 131I for child are higher than adult.
2. Optimized in-vivo monitoring program
ICRP 103 recommended that reference levels for the highest planned residual doses in emergency situations are typically in the 20 mSv to 100 mSv band of projected doses [8]. However, these levels are relatively higher than dose limit (=1 mSv y−1) of the public in planned exposure situations. In addition, Occupational Intake of Radionuclides (OIR) report issued by ICRP suggested that common practice of individual monitoring for workers whose internal dose from annual intakes could exceed 1 mSv should be done [9]. In this study, in order to provide rapid screening of internal exposure in case of radiation emergencies, a minimum detectable level was determined to set committed effective dose of 0.1 mSv which is 10 times lower than dose limit of the public corresponding with dose level in which practice of individual monitoring for workers is required.
We suggested the optimal MDAs and monitoring period summarized in Table 3 to perform the individual monitoring. 1,000 Bq for 134Cs and 137Cs, and 100 Bq for 131I were suggested as the optimal MDAs in case of radiation emergencies. And the optimal monitoring period of 134Cs and 137Cs was within 100 d and 130 d, respectively, after the event causing internal exposure, and the monitoring period of 131I was within around 20 d after the event to detect internal exposure below 0.1 mSv. These optimal levels were derived on the basis of dose levels for 10-yr old child because these levels were more conservative than those derived from adult. Moreover, we can extend the monitoring period to provide in-vivo monitoring services for adult since the MDDs for adult were lower than those for 10-yr old child.
3. Discussions on the optimized monitoring condition
Figure 6 shows MDAs of 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I measured using portable NaI gamma spectrometer. The optimal MDAs were achievable when counting time was 120 s for 137Cs and 60 s for 134Cs and 131I. However, the optimal MDAs were determined based on the committed effective dose of 0.1 mSv in this work. The optimal MDAs could be adjusted by dose level which we applied as a minimum detectable level in case of radiation emergencies. When we determine higher MDD as a detectable level for emergency response, MDAs could be increased more than the suggested optimal MDAs. Furthermore, we need to consider the increased background level which can cause an increase of MDAs of the concerned radionuclides in case of radiation emergencies.
The optimal monitoring period is also dependent on the MDD, the age group of monitoring subjects, and the type of radionuclide. For 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I, we found that the optimal monitoring period will be extended when the higher MDDs were applied for in-vivo monitoring. And adult age-group showed longer monitoring period than 10-yr old child for the concerned radionuclides in this work.
In addition, only 10-yr old child and adult were considered to represent the member of public in this work. Taking account of other age-groups would be necessary to apply in-vivo monitoring program for the member of public covering all age-groups. And this study only covers in-vivo monitoring for gamma-emitting radionuclides such as Cs and I isotopes. On the other hand, in case of suspected internal exposure for alpha- or beta-emitting radionuclides, the other monitoring method such as in-vitro radiobioassay should be applied to identify and quantify these radionuclides. And the other portable gamma spectrometers can be used instead of NaI detector even though NaI detectors are widely used as a portable gamma spectrometer.
Conclusion
In this study, we derived MDDs along with MDA using the dosimetric information of 134Cs, 137Cs, and 131I which are representative gamma-emitting radionuclides causing internal exposure of the members of public in case of radiation emergencies. Moreover, we suggested the optimal in-vivo monitoring program to be applied for radiation emergency response.
We expect that even though a reduction of counting time compared with routine monitoring usually causes the increase of MDAs of in-vivo monitoring system, it can achieve the high throughput system in case of radiation emergencies. Therefore, in-vivo monitoring program for emergency response should be designed to obtain the optimal MDAs suggested in this study. To apply this optimal in-vivo monitoring condition for rapid screening of general public, we need to perform more studies on the performance test of various types of portable gamma spectrometer such as HPGe or CZT detector and their efficiency calibration considering the posture and size of human body in the near future. In addition, detectable dose level of 0.1 mSv to be applied for emergency exposure situation can be adjusted considering various parameters such as benefits from radiation exposure, public acceptance and national regulatory guide.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences (KIRAMS), funded by Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning, Republic of Korea (1711031804/50445-2016).